Understand Heel Discomfort
Overview
Every mile you walk puts tons of stress on each foot. Your feet can handle a heavy load, but too much stress pushes them over their limits. When you pound your feet on hard surfaces playing sports or wear shoes that irritate sensitive tissues, you may develop heel pain, the most common problem affecting the foot and ankle. A sore heel will usually get better on its own without surgery if you give it enough rest. However, many people ignore the early signs of Heel Pain and keep on doing the activities that caused it. When you continue to walk on a sore heel, it will only get worse and could become a chronic condition leading to more problems.
Causes
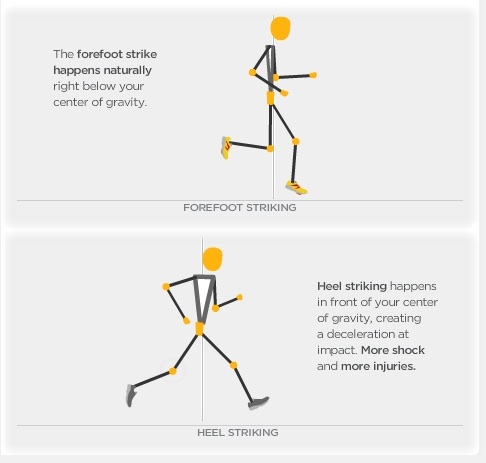
Plantar Fasciitis is the most common form of heel pain. The tears and inflammation that develop along the plantar fascia ligament result in dull aching pain or a burning sensation along the bottom of the foot. Pain becomes particularly noticeable after periods of rest, such as during the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning, or after getting up after a prolonged period of sitting. Another common form of heel pain is the development of a heel spur. A heel spur, as mentioned above, is the formation of a bony hook extending from the heel. Typically, these growths develop near the area where the plantar fascia connects to the heel bone. The repetitive pressure on the plantar fascia that results from stretching excessively away from the heel bone causes a response from our body that delivers calcium to the area. The heel pain that ensues develops from the nerves and sensitive tissue that become irritated when the bone fragment digs into the bottom of the heel. Pain may decrease after walking as the tissue in the heel gets used to the fragment and adjusts around it. However, pain will be particularly problematic following periods of rest. Strained muscle tissue may cause heel pain in several areas. A tight plantar fascia causes additional tension, particularly while exercising, placing runners and other athletes at risk if the ligament is not properly warmed up prior to exercise. Additionally, a tight Achilles tendon along the back of the foot can also add tension along the plantar fascia, resulting in possible damage, not to mention the damage and pain that can occur along the Achilles tendon itself (Achilles tendonitis). It is recommended that athletes properly stretch the foot as well as the calf in order to reduce tension on muscle and other tissue in the foot.
Symptoms
Initially, this pain may only be present when first standing up after sleeping or sitting. As you walk around, the muscle and tendon loosen and the pain goes away. As this problem progresses, the pain can be present with all standing and walking. You may notice a knot or bump on the back of the heel. Swelling may develop. In some cases, pressure from the back of the shoe causes pain.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatments to add to your stretching program include wearing good-quality shoes, icing the painful area, and massaging the arch. Do not walk barefoot; walk in shoes with good heel and arch supports such as high-quality walking or running shoes. Keep a pair of shoes next to your bed so you can put them on before taking your first step. Your doctor may recommend that you wear an additional arch support or a heel cup in the shoes. Icing your foot can help relieve pain. Rub a frozen bottle of water or an ice cup over the tender areas for five minutes two times each day. Massage your foot by rolling a tennis, golf ball, or baseball along your sole and heel. This friction massage can help break up adhesions and stretch the plantar fascia. Do this for five minutes two times each day. If you are a runner or just started a walking or running program, evaluate your training for errors such as warming up improperly, increasing mileage too quickly, running hills excessively, running on surfaces that are too hard, or wearing broken down shoes. Adjusting your training program can help relieve your pain. While recovering from heel pain, walk or jog in a pool or crosstrain by biking and swimming. These activities maintain your cardiovascular fitness without stressing your heel cord or plantar fascia. Heel pain takes time to go away. Be patient and remember that no treatment is a substitute for STRETCHING!
Surgical Treatment
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
Prevention

Wear properly fitting shoes. Place insoles or inserts in your shoes to help control abnormal foot motion. Maintain a healthy weight. Exercise and do foot stretches as they have been shown to decrease the incidence of heel pain.

Every mile you walk puts tons of stress on each foot. Your feet can handle a heavy load, but too much stress pushes them over their limits. When you pound your feet on hard surfaces playing sports or wear shoes that irritate sensitive tissues, you may develop heel pain, the most common problem affecting the foot and ankle. A sore heel will usually get better on its own without surgery if you give it enough rest. However, many people ignore the early signs of Heel Pain and keep on doing the activities that caused it. When you continue to walk on a sore heel, it will only get worse and could become a chronic condition leading to more problems.
Causes
Plantar Fasciitis is the most common form of heel pain. The tears and inflammation that develop along the plantar fascia ligament result in dull aching pain or a burning sensation along the bottom of the foot. Pain becomes particularly noticeable after periods of rest, such as during the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning, or after getting up after a prolonged period of sitting. Another common form of heel pain is the development of a heel spur. A heel spur, as mentioned above, is the formation of a bony hook extending from the heel. Typically, these growths develop near the area where the plantar fascia connects to the heel bone. The repetitive pressure on the plantar fascia that results from stretching excessively away from the heel bone causes a response from our body that delivers calcium to the area. The heel pain that ensues develops from the nerves and sensitive tissue that become irritated when the bone fragment digs into the bottom of the heel. Pain may decrease after walking as the tissue in the heel gets used to the fragment and adjusts around it. However, pain will be particularly problematic following periods of rest. Strained muscle tissue may cause heel pain in several areas. A tight plantar fascia causes additional tension, particularly while exercising, placing runners and other athletes at risk if the ligament is not properly warmed up prior to exercise. Additionally, a tight Achilles tendon along the back of the foot can also add tension along the plantar fascia, resulting in possible damage, not to mention the damage and pain that can occur along the Achilles tendon itself (Achilles tendonitis). It is recommended that athletes properly stretch the foot as well as the calf in order to reduce tension on muscle and other tissue in the foot.
Symptoms
Initially, this pain may only be present when first standing up after sleeping or sitting. As you walk around, the muscle and tendon loosen and the pain goes away. As this problem progresses, the pain can be present with all standing and walking. You may notice a knot or bump on the back of the heel. Swelling may develop. In some cases, pressure from the back of the shoe causes pain.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatments to add to your stretching program include wearing good-quality shoes, icing the painful area, and massaging the arch. Do not walk barefoot; walk in shoes with good heel and arch supports such as high-quality walking or running shoes. Keep a pair of shoes next to your bed so you can put them on before taking your first step. Your doctor may recommend that you wear an additional arch support or a heel cup in the shoes. Icing your foot can help relieve pain. Rub a frozen bottle of water or an ice cup over the tender areas for five minutes two times each day. Massage your foot by rolling a tennis, golf ball, or baseball along your sole and heel. This friction massage can help break up adhesions and stretch the plantar fascia. Do this for five minutes two times each day. If you are a runner or just started a walking or running program, evaluate your training for errors such as warming up improperly, increasing mileage too quickly, running hills excessively, running on surfaces that are too hard, or wearing broken down shoes. Adjusting your training program can help relieve your pain. While recovering from heel pain, walk or jog in a pool or crosstrain by biking and swimming. These activities maintain your cardiovascular fitness without stressing your heel cord or plantar fascia. Heel pain takes time to go away. Be patient and remember that no treatment is a substitute for STRETCHING!
Surgical Treatment
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (EST) is a fairly new type of non-invasive treatment. Non-invasive means it does not involve making cuts into your body. EST involves using a device to deliver high-energy soundwaves into your heel. The soundwaves can sometimes cause pain, so a local anaesthetic may be used to numb your heel. It is claimed that EST works in two ways. It is thought to have a "numbing" effect on the nerves that transmit pain signals to your brain, help stimulate and speed up the healing process. However, these claims have not yet been definitively proven. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has issued guidance about the use of EST for treating plantar fasciitis. NICE states there are no concerns over the safety of EST, but there are uncertainties about how effective the procedure is for treating heel pain. Some studies have reported that EST is more effective than surgery and other non-surgical treatments, while other studies found the procedure to be no better than a placebo (sham treatment).
Prevention

Wear properly fitting shoes. Place insoles or inserts in your shoes to help control abnormal foot motion. Maintain a healthy weight. Exercise and do foot stretches as they have been shown to decrease the incidence of heel pain.